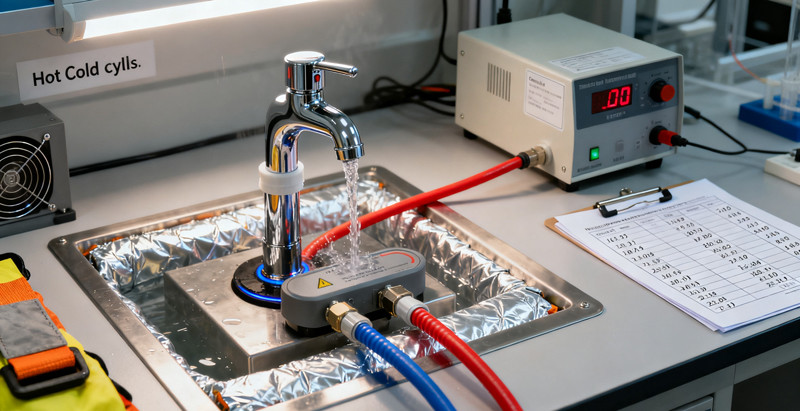
When choosing a faucet, most consumers focus on its style, brand, and features. But behind the scenes, one factor determines the faucet’s long-term appearance and customer satisfaction more than anything else — finish durability. A faucet may look beautiful on day one, but if the finish is weak, it will quickly show scratches, discoloration, water stains, or corrosion. For manufacturers, wholesalers, and retailers, testing faucet finish durability is essential to ensure quality consistency and maintain brand trust.
This guide explains how to test faucet finishes, which standards to follow, what tools are required, and how professionals evaluate long-term durability.
Why Faucet Finish Durability Matters
A faucet finish does more than add style; it protects the metal body underneath. A durable finish ensures:
-
Longer product lifespan
-
Resistance to corrosion and tarnishing
-
Protection from daily wear
-
Customer satisfaction and fewer returns
-
Better performance in harsh environments (kitchens, commercial areas, outdoor use)
Since faucets are exposed to water, cleaning chemicals, oils, minerals, and constant physical contact, the finish must withstand daily stress. Testing helps identify weaknesses before products reach the customer.
Industry-Standard Finish Tests
Professionals use specific tests to evaluate the strength of a faucet’s finish. Many of these tests align with ASTM, ISO, and ASSIST standards. Below are the most common durability tests used in the plumbing hardware industry.
1. Salt Spray (Corrosion Resistance) Test
Purpose:
To measure how well a faucet finish withstands corrosion over time.
How It Works:
The faucet or finish sample is placed inside a salt spray chamber, where it is exposed to a continuous mist of 5% sodium chloride solution.
Test Duration:
-
Basic finishes: 24–48 hours
-
High-end or PVD finishes: 200–500 hours
-
Premium commercial finishes: 800–1,000+ hours
What It Shows:
-
Rust formation
-
Pitting
-
Discoloration
-
Blistering
PVD coatings typically score highest due to their strong bond and metal-vapor deposition technology.
2. Scratch and Abrasion Test
Purpose:
To evaluate how well the faucet finish withstands physical wear.
Common Methods:
Pencil Hardness Test (ASTM D3363)
A series of pencils with different hardness levels (from 6B to 9H) are dragged across the finish. The hardest pencil that does not scratch the surface determines its scratch resistance.
Taber Abraser Test
A spinning abrasive wheel rubs the finish for hundreds or thousands of cycles to simulate long-term wear.
What It Shows:
-
Scratch visibility
-
Abrasion resistance
-
Long-term durability under heavy use
-
Performance in high-contact environments (restaurants, public restrooms)
3. Chemical Resistance Test
Purpose:
To simulate exposure to household cleaners, soaps, oils, and acidic solutions.
Process:
Common chemicals are applied to the finish, including:
-
Vinegar (acidic water deposits)
-
Bleach and chlorine-based cleaners
-
Alcohol and disinfectants
-
Detergents
-
Hard-water mineral residue
The chemicals remain in contact for 24 hours before the surface is inspected.
Evaluation Criteria:
-
Color changes
-
Cloudiness or fading
-
Surface roughness
-
Peeling or blistering
Finishes like chrome, brushed nickel, and PVD typically perform best.
4. Adhesion (Peel-Off) Test
Purpose:
To measure whether a finish is firmly bonded to the base metal.
Method:
Following ASTM D3359, a cross-hatched grid is carved into the finish. Adhesive tape is pressed over the grid and peeled away.
Results:
-
Excellent adhesion: No coating comes off
-
Weak adhesion: Finish flakes around the cuts
This test is essential for electroplated and spray-painted finishes, where adhesion is critical.
5. Hard Water Stain Resistance Test
Purpose:
To evaluate how well the finish resists mineral buildup from calcium and magnesium.
Method:
The faucet surface is repeatedly exposed to hard water and allowed to dry naturally. After multiple cycles, testers evaluate:
-
Limescale adhesion
-
Ease of cleaning
-
Surface staining
-
Gloss retention
Finishes like matte black and brushed nickel are particularly tested for stain stability.
6. UV Resistance Test
Purpose:
To simulate sun exposure, especially for outdoor faucets or pot fillers near windows.
Process:
The finish is placed in a UV chamber for extended exposure.
What It Shows:
-
Color fading
-
Surface dulling
-
Cracking
-
Yellowing
This test is essential for matte finishes, colored coatings, and outdoor products.
7. Real-World Touch and Wear Simulation
Purpose:
To simulate daily use—hands, cleaning cloths, water spots, and oils.
Methods:
-
Mechanical finger simulation (pressing and rubbing)
-
Repeated wiping with microfiber cloths
-
Exposure to lotions, soaps, and oils
-
Temperature cycling (hot vs. cold water)
Results Provide Insight Into:
-
Fingerprint resistance
-
Shine retention
-
Texture durability
-
Long-term aesthetic stability
PVD and electroplated finishes often excel in these simulations.
How Manufacturers Ensure High Finish Durability
1. Advanced Coating Technologies
PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) and multi-layer electroplating improve corrosion resistance and hardness.
2. Automated Quality Control
Robotic polishing and computerized plating ensure consistent thickness and surface uniformity.
3. Third-Party Certification
Many brands rely on SGS, INTERTEK, or NSF testing to prove compliance.
4. End-of-Line Inspection
Randomized sampling ensures every production batch meets the required durability standards.
How Retailers and B2B Buyers Can Test Finish Durability
Even after receiving products from the manufacturer, B2B buyers can perform quick checks:
-
Rub a microfiber cloth vigorously across the surface
-
Apply mild chemicals to observe reactions
-
Check for uniformity under bright light
-
Inspect edges and handle surfaces where finish failure happens first
-
Perform a small scratch test (on sample pieces only)
These small tests help confirm that the product matches the expected quality level before bulk purchasing.
Conclusion
Testing faucet finish durability is essential for ensuring quality, preventing customer complaints, and protecting your brand reputation. From corrosion and scratch resistance to chemical durability and real-world wear simulation, each test reveals important details about long-term performance. Whether you’re a manufacturer, distributor, or retailer, rigorous finish testing ensures that your faucets remain beautiful, reliable, and competitive in the market. High-quality finishes not only extend product lifespan but also build trust with homeowners and hospitality clients who demand lasting value.
 iVIGA Faucet Online Shop
iVIGA Faucet Online Shop